Recent advances in solar technology are powering the clean energy transition
- Solar affordability

Distributed solar energy is quickly becoming the cornerstone of our energy system. This didn’t happen overnight. Americans have been putting solar panels on their roofs since the 1970s. Thanks to a combination of fair solar policies and technological advances, solar has grown exponentially and prices have dropped by 99%. Solar United Neighbors (SUN) has been pushing to transform solar from a niche power source to a mainstream technology available to all communities.
Behind every solar panel is a long chain of innovations in materials, processes and labor. Recent advances in solar manufacturing have helped reduce its environmental impact and reduced costs for the final product. Read on to learn about how solar technology has advanced, and where the future of solar technology might take us!
Then versus now: more efficiency and lower costs
The evolution of solar panels over time is a testament to human innovation, smart policies, and millions of consumers choosing solar to power their communities. The most significant improvements behind solar’s dramatic growth are in the panels’ efficiency and advancements in the manufacturing of materials. Both factors have driven down solar panel costs to record lows, and lowered solar’s impact on the environment.
Solar panel efficiency measures how much of the incoming sunlight a panel is able to convert to electricity. In the early days of solar panels, only 6% of sunlight could be converted to electricity. Today, most commercial solar panels have a 15–22% efficiency rate. More efficient panels help families harvest more power from their panels and pay off their investment faster.
How solar panel components have improved over time
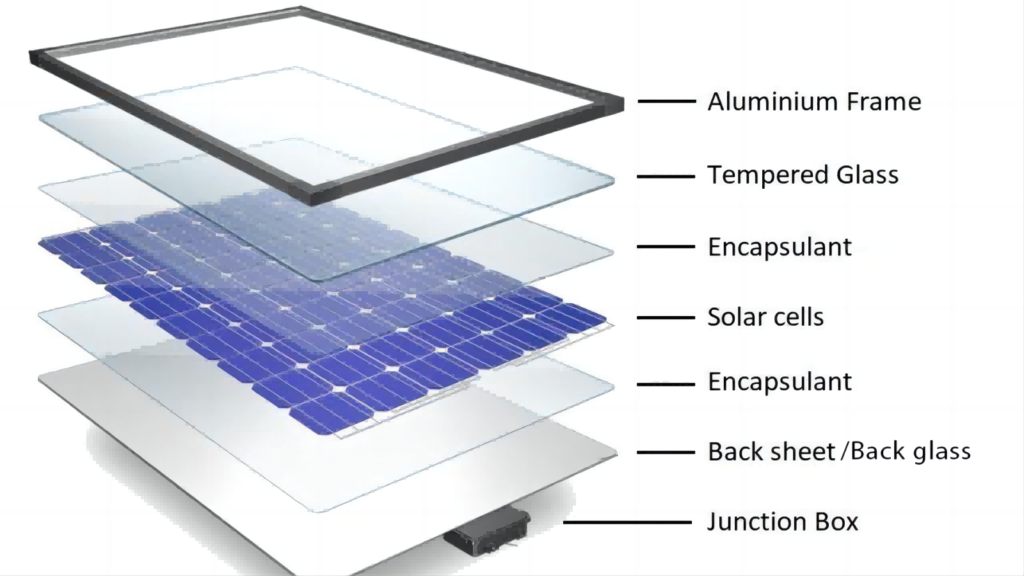
Aluminium frames
Solar panels at the scale they are today would not be possible without aluminium frames. Across the globe, people are working to make aluminum production more sustainable. Manufacturers have started using renewable energy in the smelting process and carbon-free components in the process of extracting pure aluminum. This innovation releases oxygen — a harmless gas — instead of carbon dioxide, a gas responsible for global warming. In addition, scientists are making progress in trapping extra heat energy from smelting metal, further reducing energy usage.
Decarbonizing the aluminium sector has excellent potential. The World Bank states that aluminium has nearly infinite recycling capacity, and using recycled aluminium can reduce its carbon footprint by up to twenty times.
Encapsulant materials
Encapsulant materials form protective layers around the solar cells, sealing them from moisture, dust, radiation, and physical damage. The most common type, EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate), is derived from petroleum (oil), making it non-biodegradable and reliant on non-renewable fossil fuels. While recycling EVA is possible, it is difficult. Manufacturers have innovated with plant-based materials such as bamboo, rice husks, and sugarcane ethanol. Companies are also increasing their use of renewable energy and recycling waste. These innovations are reshaping the manufacturing of EVA and establishing further sustainable practices to create clean energy.
Backsheets
Most traditional backsheets — the outermost layer of a solar panel — are currently made from plastic. These sheets are difficult to recycle and typically require energy-intensive incinerators to dispose of them. In a 2024 study, researchers tested natural fiber sheets derived from agave plants as a possible alternative. Panels produced using the natural fibers produced more power, were more efficient, and were strong enough for rooftop use. This development is a promising indicator of the path forward — sustainable manufacturing that uses less energy and less non-renewable materials.
Beyond silicon: advances in perovskite solar panels
The vast majority of solar panels are made from silicon, but solar panels that use perovskite — a family of minerals — could be a big breakthrough. Perovskite has lots of advantages over silicon: it’s ultra thin, it’s inexpensive to make, and it can convert more light to electricity. In 2024, a laboratory in Oxford, England, broke the world record for the most efficient residential-scale perovskite solar panel — an unprecedented 26.9% efficiency!
Things are just getting started for perovskite solar panels. Right now, scientists are still testing them in labs for durability and environmental impact. But there’s real hope about a new low-cost, scalable technology entering the solar market in the near future.
The carbon footprint of solar panels
Solar panels themselves emit no harmful gases. Switching from fossil fuels to solar can reduce health problems associated with air pollution and climate change.
The carbon footprint from manufacturing is small, and continues to drop. Between 2011 and 2021, carbon emissions from solar panel manufacturing dropped 45%. Compared to 2007, solar panels today use 67% less silver — the most expensive materials in solar panels — and the process to make silicon uses 50% less energy. Though panel production uses energy, it only takes about 12 months for a solar panel to produce more energy than was used to create it. That’s helped to drive down the cost of solar panels and lessen its environmental impact.
Bringing solar power to the people
There’s a lot to get excited about in the world of solar technology. However, high startup costs for solar panels still make it difficult for many communities to access the latest technologies. Fair solar policies can help more families reap the cost-saving and environmental benefits of solar. Learn how to join our solar movement by checking out ongoing actions near you!
Join the fight for more affordable solar
Get the latest on solar straight to your inbox.
Fight for your solar rights.
Everyone has the right to go solar. Spread the sunshine nationwide and in your local community by taking action, joining events, and more.